Fabric Textile Printing: A Complete Guide
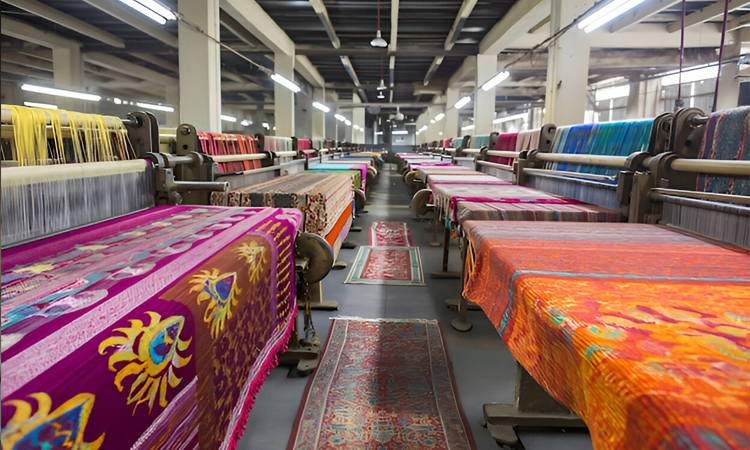
Fabric textile printing has become an essential part of the textile and fashion industry. Whether for clothing, home décor, or industrial textiles, fabric textile printing allows manufacturers and designers to bring color, patterns, and creativity to plain fabrics. In this guide, we’ll explore what fabric textile printing is, the types, processes, advantages, and applications.
What is Fabric Textile Printing?
Fabric textile printing is the process of applying color, patterns, or designs to fabric using various methods and techniques. Unlike dyeing, which colors the entire fabric, fabric textile printing applies designs only where needed, allowing for more intricate patterns and multicolored designs.
The process is widely used in clothing, upholstery, and technical fabrics. With fabric textile printing, plain textiles are transformed into visually appealing products that meet fashion trends and consumer preferences.
Types of Fabric Textile Printing
There are several methods of fabric textile printing. Each method has unique characteristics and is suitable for different fabrics and designs. Here are the main types:
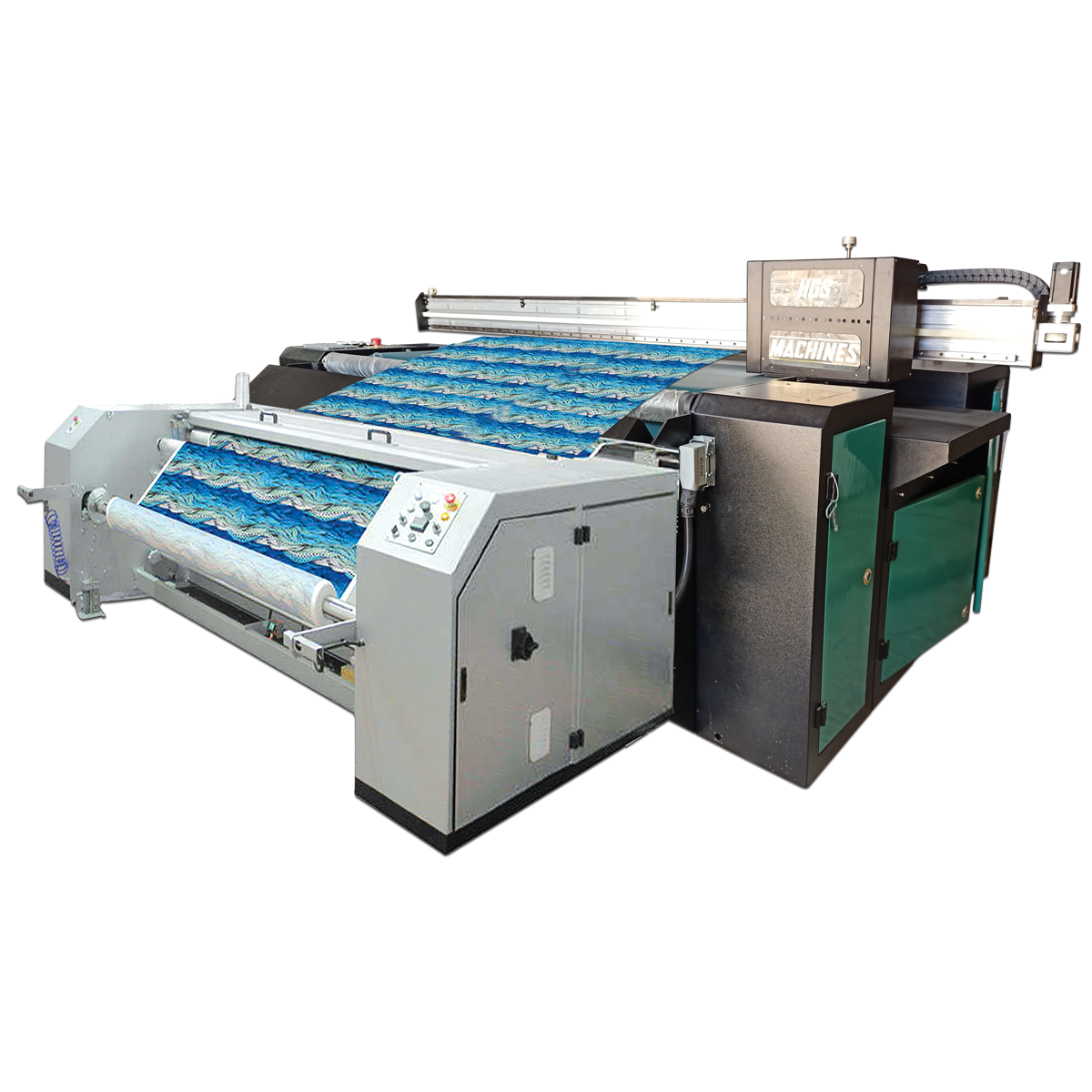
1. Screen Printing
Screen printing is one of the oldest and most common fabric textile printing techniques. In this process, a stencil or “screen” is used to apply ink directly onto the fabric. Each color requires a separate screen, making multi-colored designs more complex.
Advantages: High durability, vibrant colors, ideal for large patterns.
Best for: Cotton, polyester, and blend fabrics.
2. Digital Printing
Digital printing is a modern method where designs are printed directly onto the fabric using inkjet technology. This allows highly detailed patterns and color gradients.
Advantages: Quick turnaround, suitable for small batches, intricate designs possible.
Best for: Cotton, silk, polyester, and synthetic fabrics.
3. Rotary Printing
Rotary printing uses a cylinder to transfer dye onto fabric as it moves through the machine. This method is efficient for large-scale production.
Advantages: Fast production, continuous patterns, cost-effective for bulk orders.
Best for: Cotton, polyester, and blended fabrics.
4. Heat Transfer Printing
Heat transfer printing involves transferring designs from paper onto fabric using heat and pressure. It is widely used for promotional materials, sportswear, and custom products.
Advantages: Easy customization, vibrant colors, small to medium production runs.
Best for: Polyester, cotton-polyester blends, and nylon fabrics.
5. Block Printing
Block printing is a traditional method where hand-carved wooden blocks are dipped in dye and pressed onto the fabric.
Advantages: Artistic, handmade appearance, eco-friendly if natural dyes are used.
Best for: Cotton, silk, and linen fabrics.
The Fabric Textile Printing Process
The process of fabric textile printing generally follows a series of steps. While the steps may vary based on the printing method, the basics remain the same.
Step 1: Fabric Preparation
Before printing, fabrics are pre-treated to remove impurities, oils, or sizing agents. This ensures better dye absorption and color fastness. Pre-treatment may involve washing, bleaching, or applying a chemical coating.
Step 2: Design Preparation
Designs are created digitally or manually. For screen printing, stencils or screens are prepared. For digital printing, files are formatted in high resolution. Fabric textile printing requires precise designs to achieve accurate colors and patterns.
Step 3: Printing
The prepared design is applied to the fabric using the chosen method. For example, in screen printing, ink passes through a mesh screen. In digital printing, ink is sprayed directly onto the fabric.
Step 4: Fixation
After printing, the color must be fixed on the fabric. Fixation ensures that the print remains durable through washing and wear. Methods vary by printing type and dye used, including steaming, heating, or chemical treatment.
Step 5: Finishing
Finally, the printed fabric undergoes finishing processes like washing, steaming, or coating to improve texture, softness, and colorfastness. Finished fabrics are ready for cutting, sewing, or other manufacturing steps.
Advantages of Fabric Textile Printing
Fabric textile printing offers multiple benefits for manufacturers, designers, and consumers. Some key advantages include:
Creative Flexibility – Fabric textile printing allows for intricate designs, patterns, and color combinations that dyeing alone cannot achieve.
Cost-Effective for Short Runs – Digital and heat transfer printing make small-batch production affordable.
High-Quality Prints – Modern techniques ensure detailed designs and vibrant colors.
Eco-Friendly Options – Many methods use water-based inks and natural dyes, reducing environmental impact.
Customization – Fabric textile printing enables unique, personalized designs for fashion, home décor, and promotional products.
Applications of Fabric Textile Printing
Fabric textile printing is versatile and used across many industries. Some popular applications include:
Fashion and Apparel
Printed fabrics are widely used in the fashion industry for dresses, shirts, skirts, scarves, and other garments. Designers rely on fabric textile printing to create unique patterns and seasonal collections.
Home Textiles
Fabric textile printing is common in home décor products such as curtains, bedspreads, cushions, and upholstery fabrics. Printed fabrics add aesthetic appeal and can match any interior theme.
Technical Textiles
Technical fabrics for sportswear, medical textiles, and industrial applications also use fabric textile printing. For example, heat transfer printing is used for logos on sports jerseys, while durable inks are used for industrial fabrics.
Promotional Products
Customized printed fabrics are used for promotional items like tote bags, banners, and branded clothing. Fabric textile printing allows businesses to convey their brand effectively.
Tips for Choosing the Right Fabric for Printing
Not all fabrics are equally suitable for printing. Here are some tips:
Cotton – Soft, breathable, and ideal for most printing methods.
Polyester – Durable, lightweight, and works best with sublimation or heat transfer printing.
Silk – Smooth and luxurious, suitable for digital or screen printing.
Blends – Fabrics like cotton-polyester blends offer versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Common Challenges in Fabric Textile Printing
Even though fabric textile printing is popular, there are some challenges:
Color Accuracy – Achieving exact color matches can be difficult across batches.
Fabric Shrinkage – Some fabrics shrink after printing, affecting design alignment.
Durability – Prints must withstand washing, sunlight, and wear without fading.
Environmental Concerns – Some dyes and chemicals can be harmful if not managed responsibly.
Trends in Fabric Textile Printing
The fabric textile printing industry is evolving rapidly. Here are some current trends:
Digital Printing Dominance – Digital printing continues to grow due to its speed and customization capabilities.
Eco-Friendly Printing – Water-based inks and natural dyes are replacing harmful chemicals.
Smart Fabrics – Printing on fabrics with conductive inks for wearable technology is emerging.
On-Demand Printing – Small batch and personalized orders are becoming mainstream.
FAQ – Fabric Textile Printing
1. What is fabric textile printing?
Fabric textile printing is the process of applying colors, patterns, or designs onto fabrics using techniques like screen printing, digital printing, heat transfer, or block printing. Unlike dyeing, it allows precise placement of designs.
2. What types of fabric textile printing are available?
The main types of fabric textile printing include:
Screen Printing – Uses a stencil to apply ink through a mesh.
Digital Printing – Prints designs directly onto fabric using inkjet technology.
Heat Transfer Printing – Transfers designs from paper to fabric using heat.
Rotary Printing – Uses a cylinder for continuous fabric printing.
Block Printing – Hand-carved wooden blocks are used to stamp designs.
3. Which fabrics are best for fabric textile printing?
Cotton – Soft, breathable, and ideal for most printing methods.
Polyester – Works best with sublimation or heat transfer printing.
Silk – Smooth surface, suitable for detailed designs.
Blended Fabrics – Cotton-polyester blends offer flexibility and durability.
4. How does digital fabric textile printing work?
Digital printing applies ink directly to fabric using inkjet printers. The fabric is usually pre-treated, and the design is printed in high resolution. After printing, the fabric is heat-treated or steamed to fix the colors.
5. What are the benefits of fabric textile printing?
High-quality, detailed designs
Creative flexibility for patterns and colors
Cost-effective for small and medium batches